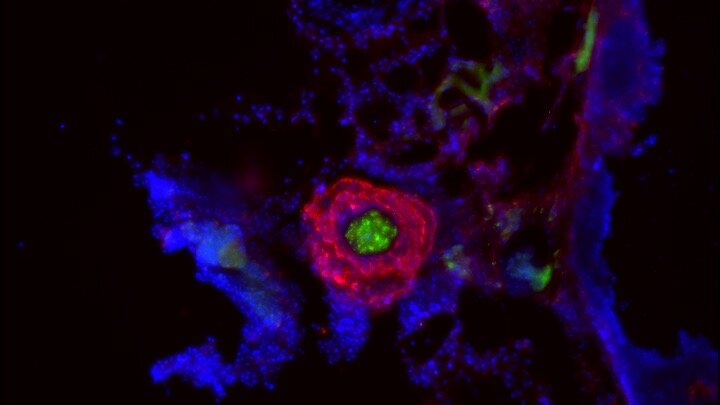
Tuberculosis pathogenesis and host-directed therapies
Novel host-directed therapies against tuberculosis (TB) are required to overcome the threat posed by multidrug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Pathogenic mycobacteria modify or co-opt host responses to infection to successfully establish persistent granulomatous infections. We have shown that reversing the vascular pathologies caused by mycobacterial infections helps control infection.
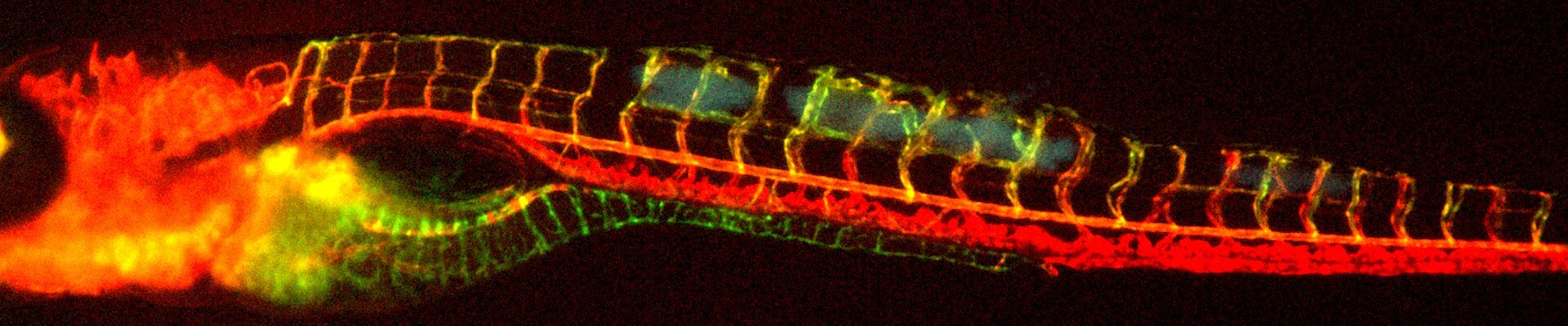
Seeing is believing: granuloma angiogenesis
Live imaging infection-induced angiogenesis in a M. marinum-infected zebrafish embryo
Green=blood vessels, red=red blood cells, blue=bacteria
Non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections
Our understanding of NTM infection pathogenesis and effective treatment strategies are limited. We have found infecting adult zebrafish with Mycobacterium abscessus provides a great model of persistent infection.
This is a brand new avenue of research where the zebrafish promises to deliver unique insights into M. abscessus pathogenesis.
Current projects
The zebrafish provides a powerful platform to literally look at mycobacterial infections in a new light. Current mycobacterial infection projects include:
Hijacking of host immune responses by pathogenic mycobacteria
Tuning host immunity to do a better job
Healing of mycobacterial granulomas

